Section: Software and Platforms
The Polychrony toolset and its hypertext source documentation
Participants : Loïc Besnard, Thierry Gautier, Paul Le Guernic.
The Polychrony toolset is an Open Source development environment for critical/embedded systems. It is based on Signal, a real-time polychronous dataflow language. It provides a unified model-driven environment to perform design exploration by using top-down and bottom-up design methodologies formally supported by design model transformations from specification to implementation and from synchrony to asynchrony. It can be included in heterogeneous design systems with various input formalisms and output languages.
The Polychrony toolset provides a formal framework:
-
to validate a design at different levels, by the way of formal verification and/or simulation,
-
to assemble heterogeneous predefined components (bottom-up with COTS),
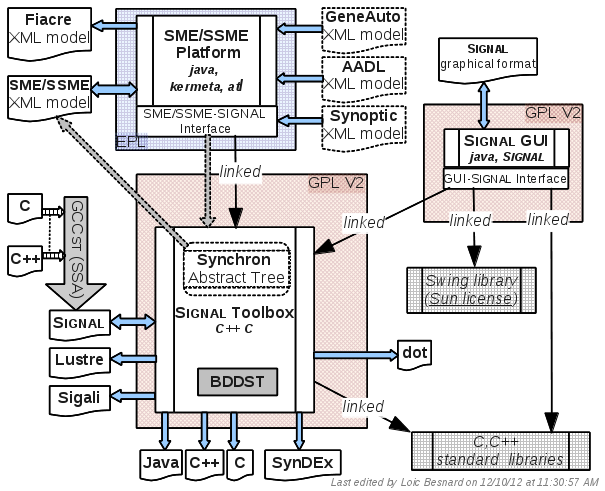
The Polychrony toolset contains three main components and an experimental interface to GNU Compiler Collection (GCC):
-
The Signal toolbox, a batch compiler for the Signal language, and a structured API that provides a set of program transformations. The Signal toolbox can be installed without other components. The Signal toolbox is distributed under GPL V2 license.
-
The Signal GUI, a Graphical User Interface to the Signal toolbox (editor + interactive access to compiling functionalities). The Signal GUI is distributed under GPL V2 license.
-
The SME/SSME platform, a front-end to the Signal toolbox in the Eclipse environment. The SME/SSME platform is distributed under EPL license.
-
GCCst, a back-end to GCC that generates Signal programs (not yet available for download).
In 2013, to be able to use the Signal GUI both as a specific tool and as a graphical view under Eclipse, the code of the Signal GUI has been restructured in three parts: a common part used by both tools (28 classes), a specific part for the Signal GUI (2 classes), a specific part for Eclipse (2 classes). Such a structuration facilitates the maintenance of the products.
The Polychrony toolset also provides:
The building of the Signal toolbox is managed using the CMake utility (http://www.cmake.org ). It is used to ensure the portability on the different operating systems (CMake generates native makefiles). For the same reason, in 2013, we have integrated the management of the tests of the Signal batch compiler under CMake (using CTest).
The Polychrony toolset can be freely downloaded on the following web sites:
-
The Polychrony toolset public web site: http://www.irisa.fr/espresso/Polychrony/index.php . This site, intended for users and for developers, contains downloadable executable and source versions of the software for differents platforms, user documentation, examples, libraries, scientific publications and implementation documentation. In particular, this is the site for the new open-source distribution of Polychrony.
-
The Inria GForge: https://gforge.inria.fr . This site, intended for internal developers, contains the whole sources of the environment and their documentation.
In 2012, during the OPEES project, we have integrated Polychrony on the Polarsys Experimental Eclipse platform, a new industry collaboration to build open source tools for safety-critical software development. In 2013, the integration to the actual Eclipse Polarsys platform (http://www.polarsys.org ) has been started. The proposal project is available at http://www.eclipse.org/proposals/polarsys.polychrony . The creation of a new Polarsys project (as defined in the Eclipse Development Process) is decomposed into several steps (before the first release): project proposal, community review, trademark review, creation review, provisioning, initial contribution. For trademark reasons, Polychrony is called POP as Polarsys Project (POP, a polychronous modeling environment on Polarsys). At the end of 2013, we are at the “provisioning” step. It will be provisioned as soon as the employer consent (Inria, CNRS) form will be signed.
The Polychrony toolset currently runs on Linux, MacOS and Windows systems.
Dassault Systèmes, supplies a commercial implementation of Polychrony, called RT-Builder, used for industrial scale projects.
As part of its open-source release, the Polychrony toolset not only comprises source code libraries but also an important corpus of structured documentation, whose aim is not only to document each functionality and service, but also to help a potential developer to package a subset of these functionalities and services, and adapt them to developing a new application-specific tool: a new language front-end, a new back-end compiler. This multi-scale, multi-purpose documentation aims to provide different views of the software, from a high-level structural view to low-level descriptions of basic modules. It supports a distribution of the software “by apartment” (a functionality or a set of functionalities) intended for developers who would only be interested by part of the services of the toolset.
A high-level architectural view of the Polychrony toolset is given in Figure 7 .